Fibroids and Gynae Cancers: Cervical, Ovarian, Uterine, Vaginal, Vulvar, Skene’s Glands, Pap Smears
Fibroids and Gynae Cancers: Cervical, Ovarian, Uterine, Vaginal, Vulvar, Skene's Glands, Pap Smears
Facing challenges like fibroids or gynecological cancers (cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, vulvar, Skene's Glands)?RoyalDocline Clinic specializes in personalized solutions. Our OBGYN expert provides expert guidance, offering advanced diagnostics and customized treatments. From routine Pap smears to managing complex conditions, trust RoyalDocline for dedicated assistance. Prioritize your well-being—schedule your consultation today!
Fibroids:
Evaluation:
- Physical Examination:
- Pelvic exam to check for the presence, size, and shape of fibroids.
- Imaging:
- Ultrasound, MRI, or hysteroscopy to visualize and determine the location and size of fibroids.
3. Biopsy (if needed):
- Rarely, a biopsy may be done to rule out cancer if the appearance of the fibroid is concerning.
Treatment:
- Watchful Waiting:
- Monitoring fibroids without treatment if they are small and not causing symptoms.
- Medications:
- Hormonal medications (birth control pills, GnRH agonists) to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce symptoms.
- Non-Invasive Procedures:
- Uterine artery embolization to block blood flow to fibroids, reducing their size.
- Surgical Options:
- Myomectomy to remove fibroids while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy for severe cases or when fertility is not a concern.
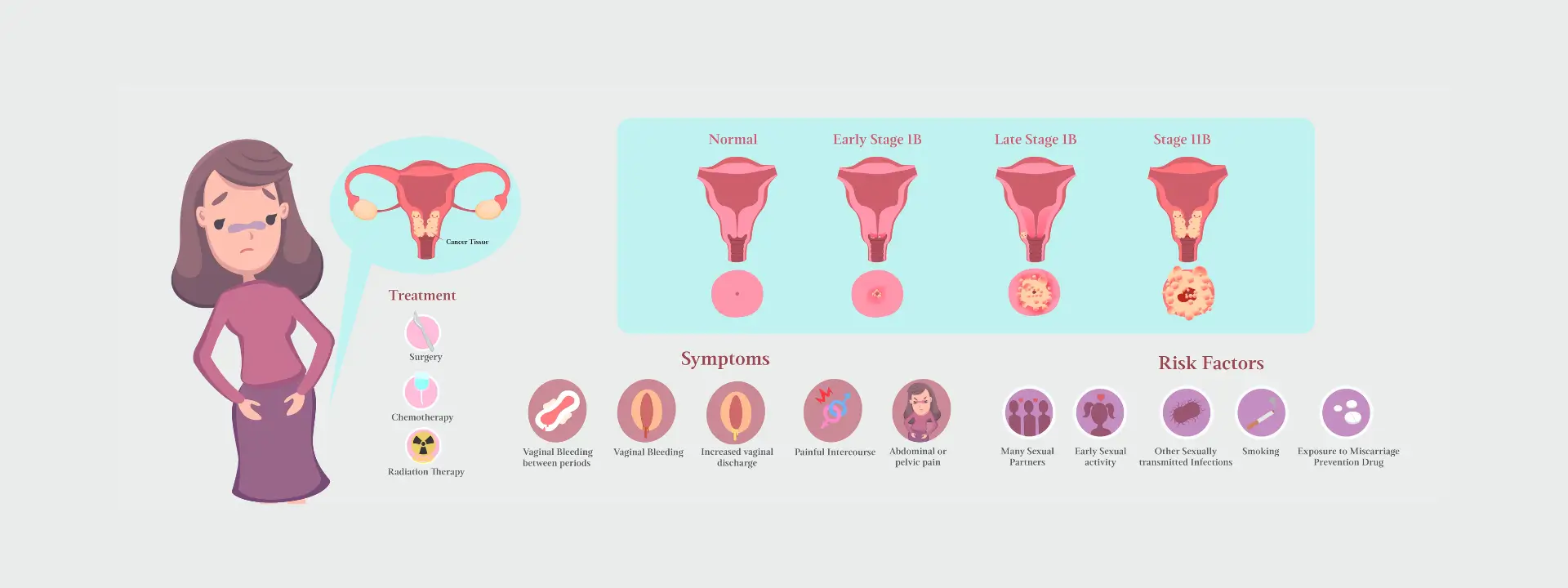
Gynecological Cancers:
Cervical Cancer:
Evaluation:
- Pap Smear:
- Regular Pap smears to detect abnormal cervical cells.
- HPV Testing:
- Testing for high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) strains, a common cause of cervical cancer.
- Colposcopy:
- Visual examination of the cervix using a colposcope if abnormalities are detected.
- Biopsy:
- If abnormal cells are found, a biopsy may be performed for further evaluation.
Treatment:
- Cryotherapy or LEEP:
- Removal of abnormal cervical tissue in early stages.
- Surgery:
- Conization or hysterectomy for more advanced cases.
- Radiation and Chemotherapy:
- Used in more advanced cases or after surgery.
Ovarian Cancer:
Evaluation:
- Pelvic Examination:
- To check for ovarian abnormalities.
- Imaging:
- Ultrasound, CT, or MRI to visualize the ovaries.
- Blood Tests:
- CA-125 blood test to detect a tumor marker associated with ovarian cancer.
Treatment:
Surgery:
- Removal of the tumor (debulking) or complete hysterectomy.
Chemotherapy:
- Often recommended post-surgery.
Uterine Cancer:
Evaluation:
Endometrial Biopsy:
- Sampling of the uterine lining to detect abnormal cells.
Imaging:
- Ultrasound, CT, or MRI to visualize the uterus.
Treatment:
Surgery:
- Hysterectomy, often with removal of nearby lymph nodes.
Radiation and Chemotherapy:
- Used in advanced cases or after surgery.
Vaginal and Vulvar Cancers:
Evaluation:
Physical Examination:
- Inspection for abnormalities or lesions.
Biopsy:
- Removal and examination of tissue for cancer cells.
Treatment:
Surgery:
- Removal of cancerous tissue.
Radiation and Chemotherapy:
- Used in advanced cases or after surgery.
Skene’s Glands (Female Prostate):
Evaluation:
Physical Examination:
- Palpation to check for tenderness, swelling, or abnormalities.
Imaging:
- Ultrasound or MRI for visualization.
Treatment:
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adequate hydration and maintaining good genital hygiene.
Medical Management:
- Antibiotics if infection is present.
Surgical Options:
- In some cases, drainage or removal of infected glands may be necessary.
Pap Smears:
Evaluation:
Regular Screening:
- Pap smears at recommended intervals to detect abnormal cervical cells.
HPV Testing:
- Testing for high-risk HPV strains, particularly for women over 30.
Treatment:
Colposcopy and Biopsy:
- Follow-up procedures if abnormalities are detected.
Treatment of Precancerous Lesions:
- Cryotherapy, LEEP, or other methods to remove abnormal cells.
Regular gynecological exams, screenings, and prompt evaluation of symptoms are crucial for the early detection and effective management of these conditions.
Related Services

Menopausal P...
Experience superior Menopause car...

Menstrual Dis...
Receive specialized care for Menstrual Pr...

Infertility Evalu...
At RoyalDocline, our expertise is dedicated to as...

Polycystic Ova...
Navigating PCOS complexities? Seek specialized...

